Growth Hacking Jargon can be confusing to even the most established marketers. With ideas and acronyms created and discovered every day, it can be hard to keep up with the overwhelming amount of terminology.
In this post, we’ll run you through the 99 most important Growth Hacking Jargon terms, providing a brief description of what each one means for a fully fledged digital marketing glossary.
Let’s dive right in.
Table of Contents
General Growth Hacking Jargon
First up, we’ll cover some of the more common and general growth hacking jargon. Many of these terms will be familiar to you unless you’re brand new to the field, but it never hurts to double-check to make sure you’re using terminology in the right context.
1. Growth Hacking
Starting with the most obvious, Growth hacking is a term used for digital marketing techniques that focus on rapid growing a business while using a minimal amount of resources.
It is done through continuous experimentation and creative usage of the most suitable online marketing channels, digital tools, and strategies for a company.
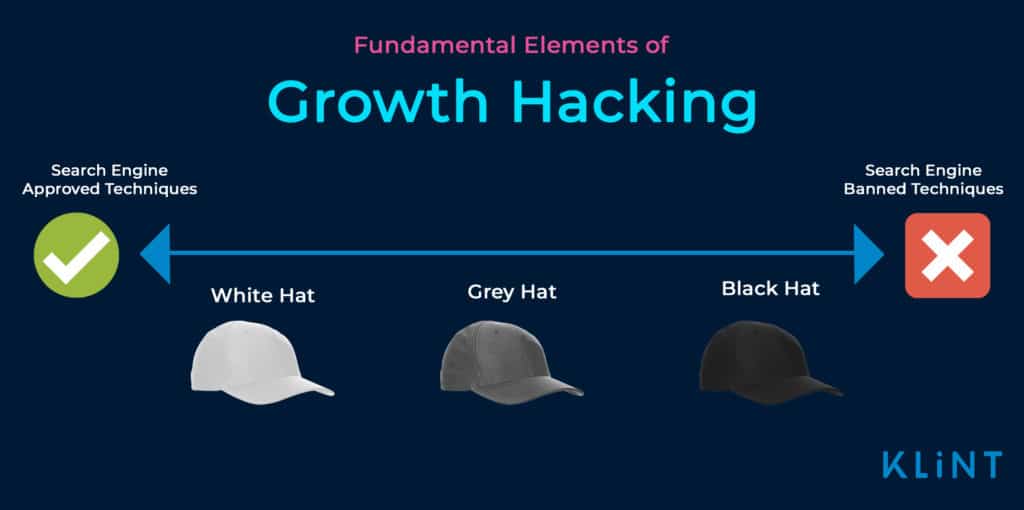
2. Black Hat SEO
Black Hat growth hacking involves using marketing and SEO techniques which breach the rules and regulations of search engines.
Many SEO experts advise against using black hat SEO, as it often comes with large penalties from search engines which affect the digital presence and ranking of the company responsible.
Black-Hat SEO Techniques include practices like:
- Keyword stuffing
- Invisible text
- Paid links
- Spam commenting
- Duplicate content
3. White Hat SEO
White Hat SEO hacks are legitimate SEO techniques that search engines regard as acceptable ways to improve your site’s performance.
These techniques, when applied correctly, can help improve your site ranking in search engines.
Useful White Hat SEO Techniques are:
- Keyword Research
- Link Building
- Fast loading speeds
- Unique and Relevant content
- Image optimization
- Structured data
- Site navigation ease
4. Grey Hat SEO
As you would expect, Grey Hat SEO is somewhere between white hat and black hat techniques.
Grey Hat techniques aren’t explicitly banned, but if you don’t know what you’re doing they can get you into to hot water with Google or other search engines.
Techniques include practices like cloaking or social media automation.
5. SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Search Engine Optimization is the practice used by growth hackers and digital marketers to enhance organic traffic to a site or page. SEO includes a wide range of practices and techniques, from link building and keyword targeting to meta descriptions and alt text.

Over the past 10-15 years, SEO has become the established set of “rules” that governs which content ranks higher up the page on search engines. The benefit for higher ranking for businesses is increased traffic to their sites.
Of course, this means that SEO is highly competitive, with new techniques and theories used by companies every day to rank more highly than their rivals.
6. On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO refers to the optimization of web pages you control to increase your ranking.
It involves content quality, technical optimization, and a well-designed user experience (UX). Each of these factors give search engines the ability to determine the ranking position of a page.
7. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO or Off-Site SEO is a process whereby growth hackers strive to improve the ranking of a website by actions taken outside of the webpage. It includes the improvement of relevance, trustworthiness, and authority.
Improved off-page SEO is usually achieved by:
- Article submissions
- Contributions as a guest author
- Social media engagement
- Influencer outreach
- Creating shareable content
8. Voice Search
Voice Search is a relatively new technology that allows users to run searches by speaking into their smartphones, computers, or even IoT adapted home devices.
The usage of this technology has started to grow exponentially in the past few years, and it has become a major SEO factor.
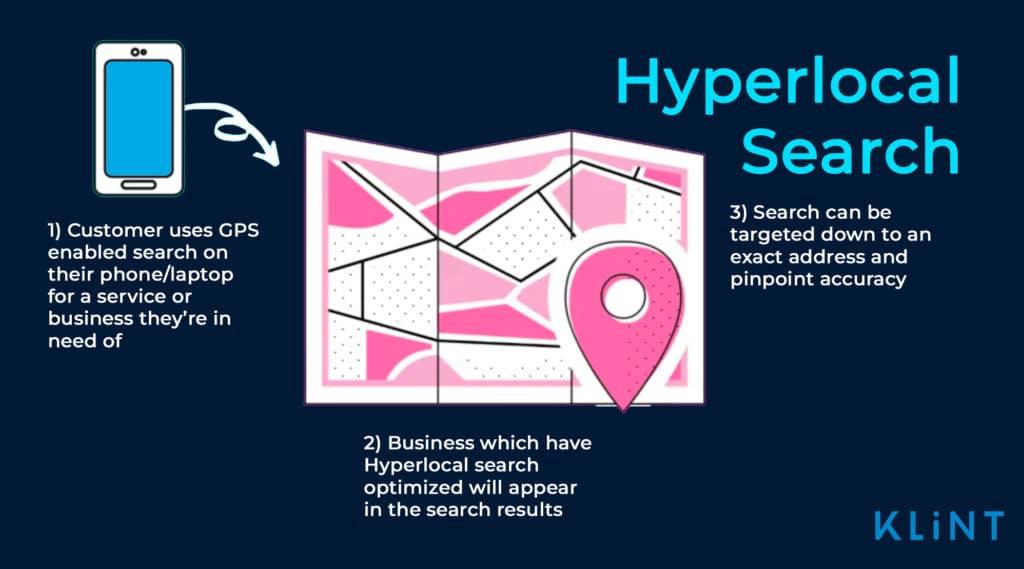
9. Hyperlocal Search Optimization
Hyperlocal search optimization works in the same way as regular SEO, but it is more focused on a specific geographical area. GPS tracking is required on the search device for hyperlocal search to be effective.
10. SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
SEM is a way of paying search engines to generate traffic to your website. It offers quick wins compared to SEO, as it displays adverts and links to your website in paid-for spaces on a search engine to attract visitors to your site.
However, SEM does not build your online “reputation” in the long term, and it can require significant financial investment.

SEM offers large benefits to advertisers as they are able to place their advert in front of customers at the exact moment they are looking to purchase a product – namely when they are searching for something.
SEO & SEM each have their own pros and cons, and as a result most of the best growth hackers and marketers utilize both.
11. Search Engine Result Pages (SERP)
Search engine result pages are the pages that appear on your screen when a search engine displays the results of your search. The different websites that are shown on these pages can be organic results or paid advertisements.
Increasingly, it is not necessary to click on specific results as Google shows answers to questions in “snippet” sections. Searches that don’t result in clicks are known as “zero-click searches”.
12. Geofencing Growth Hacking
Geo-fencing growth hacking is a growth hack invented in 2015. Geofencing allows marketers to determine a specific geographical area that functions as a digital marketing opportunity.
When users with digital devices such as mobile phones, tablets, or laptops enter the marked geographical area, they receive personalized content.
One example of this is when mobile network providers send welcome SMS’s when a user enters one country from another.
Link Growth Hacking Jargon
Backlinks, and link-building, are an essential aspect of successfully improving your site and page rankings. As such, there is a wide range of terminology and growth hacking jargon associated with it.
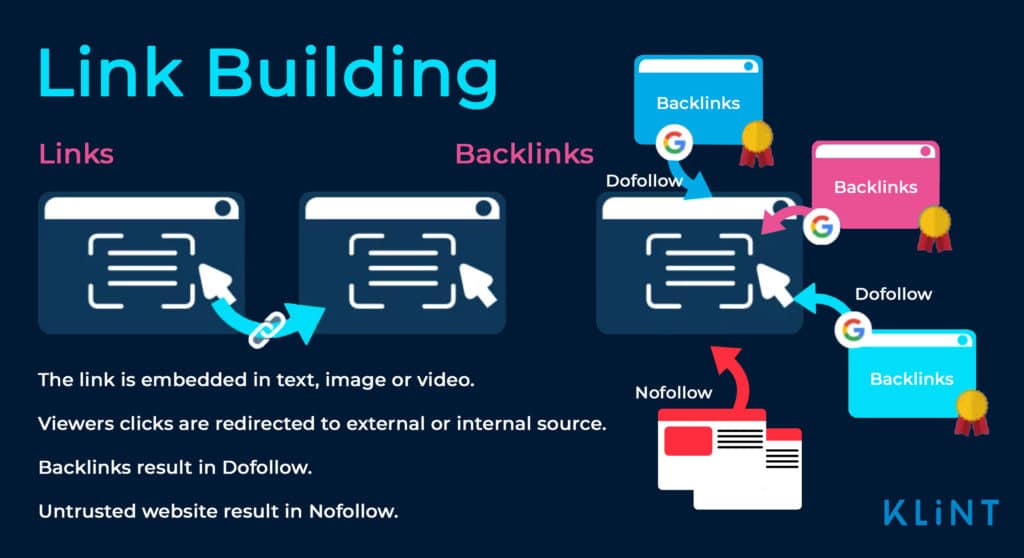
13. Backlinks
Backlinks are a major element of SEO.
When another company places a link within their content that points to your webpage, it’s referred to as a backlink. It indicates to Google that the information that you shared is credible and trustworthy.
This is one way in which you build your online reputation and get better rankings.
14. Link Building
Put simply, link building is the techniques and strategies used by growth hackers and marketers to increase the number of backlinks they have from other websites.
Link building techniques include:
- blogging
- guest posting
- site listings
- Email outreach
The more backlinks your site and pages have, the more likely you are to rank in the top page for different keywords.
15. No-follow
No-follow links are links that refer to your website as a source of information, but do little to improve your ranking.
They are used when the linking website does not want to pass authority on to the linked website. Some examples of when this may happen include affiliate links or sponsored posts.
While do-follow backlinks are generally more desirable that no-follow backlinks, a natural backlink profile for a website will include both.
16. Do-follow
Do-follow links are links that count as references received by other websites and they indicate that your website has quality content.
When another webpage links to your site, it usually means that they found relevant information that they believe to be worthwhile.
Do-follow backlinks directly and positively influence your site’s ranking.
17. Organic Traffic
Organic traffic refers to all traffic that a website receives that it doesn’t pay for. For example, if someone searched for the term ‘customer perception’, and clicked on Klint’s customer perception post, then it would count as organic traffic.
SEO techniques like backlink building and keyword research are used to improve organic traffic.
Growth Hacking Jargon Around…Keywords
Much like backlinks, keywords act as one of the essential pillars of search engine optimization. It’s extremely difficult to improve your site and page rankings without using some form of keywords or keyword research.
In this section, we break down some of the growth hacking jargon within this area of SEO.
18. Keyword Stuffing
In the early days of search engines, if you wanted a website to rank for a specific keyword, you just had to include the same word as many times as possible.

This resulted in hundreds of thousands of blog posts reaching the number one spot that didn’t really make sense or answer reader questions.
Today, this is known as keyword stuffing and is regarded as a form of black hat SEO that negatively affects your site ranking.
Many content management systems offer software that detects and highlights accidental keyword stuffing.
19. Long-tail keywords
Long tail keywords are phrases that are more specific and targeted than the more generic short keywords.
By implementing these phrases into a website or a piece of content, it is more likely to be displayed for users who searched for the exact term.
Long-tail keywords nearly always have a lower search volume than short tail keywords, however as a result they are usually less competitive.
For example, instead of trying to rank for the short-tail keyword ‘shoes’, it may make more sense to target the long-tail keyword ‘white training shoes with black laces ‘, which will get fewer searches.
Many growth hackers and digital marketers will target both long-tail and short-tail keywords.
20. Keyword Relevance
Keyword relevancy tells you how much your chosen words relate to your website and brand. The more relevant phrases you use, the greater your chance of attaining a higher ranking.
21. Keyword Search Volume
Keyword search volume is the number that indicates the popularity and searchability of a keyword.
Keyword tools such as Google Keywords and Ahrefs provide insights into the volume of keywords based on searches.
Usually a promising search volume starts at approximately 700-800 searches per month. However, it can change based on seasons, the target industry and the competition for the keyword.
22. Keyword Competition
Keyword competition is an evaluation of a keyword or phrase that shows how difficult it is to rank on Google and other search engines.
High-competition keyword often have a high search volume or very specific keyword intent that implies a readiness to buy. Locating high-volume keywords that have a low keyword competition is an important part of SEO.
23. Keyword Intent
Keyword intent is growth hacking jargon that describes the reason someone is searching for something, which can have a big difference on whether they will click on your site.
We distinguish four different types of keyword intent:
- Commercial Intent: Users are searching to decide whether to buy. Phrases just as “buy now”, “discount”, “deals” that indicate a strong motivation for purchasing.
- Informational Intent: Users who search for terms just as “How to..”, “Best way to..”, “How can I..” are usually searching for an informative solution for whatever question or pain point they have. While this group may be willing to buy, it is less likely than other types of keyword intent.
- Transactional Intent: People who are led by transactional intent are usually between the commercial and transactional phase. They are both interested in buying and reading more about the solution for their problem. Key phrases under the umbrella of transactional intent often include “reviews”, “best company for..”, “..vs..” and similar terms.
- Navigational Intent: Navigational intent driven users know exactly what they want and who they are looking for. This form of search includes brand names.
It’s vital to consider keyword intent when performing SEO.
24. LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing)
LSI keywords are words that are closely related to your topic.
It is an important factor if you want to build content with strong keyword density.
As an example, if you wanted to rank for “Content marketing services” you’d have to include phrases just as “amplification”, “link building”, “do-follow” and “no-follow” in your content.
25. Keyword ROI
Keyword Return-on-Investment (ROI) is the return on your financial investment while trying to rank for a keyword.
It depends on factors such as keyword intent, keyword difficulty or keyword competitiveness.
26. Keyword Proximity
A search phrase is a combination of keywords. Keyword proximity indicates the distance between the individual search terms within the phrase.
The smaller the distance between the keywords, the more relevant it becomes and the better ranking it’s going to have on search engines.
27. KEI (Keyword Effectiveness Index)
These are keywords which show potential to be searched for, are relevant for your brand, and can bring traffic to your website.
Usually, words or phrases with a 70+ KEI ranking are considered good.
Growth Hacking Jargon About…Metrics
It can be particularly tricky to remember the meaning behind different metrics within marketing and growth hacking, as they are often abbreviated to acronyms.
This section covers the most crucial growth hacking jargon about metrics within marketing, and the acronyms you will come across most frequently.
28. Bounce Rate
Within site optimization, bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave your site after only visiting one page. It shouldn’t be confused with email bounce rate, which refers to the percentage of marketing emails which are undeliverable.
Bounce rate on websites can have a number of different causes, including:
- Low page speed
- Not enough valuable information
- Poor readability

Internal links that point toward other content on your site, like this one, are one way of reducing your bounce rate. Likewise, Call-to-Action buttons have the same effect and images and videos can keep your visitors directly on your page, raising interest to visit other sections.
If you want to calculate your bounce rate, simply divide the total number of page visits by the total number of bounces.
This ‘Guide to Bounce Rate Analytics’ can help you to navigate and audit your bounce rate metrics.
29. Vanity Metrics
Vanity metrics are metrics which, while interesting, serve little value in isolation. Metrics Click-Through-Rates (CTR) or impressions, while interesting, do not give a clear picture of performance.
Many companies now analyze actionable metrics such as conversions, acquisitions, and behaviours.
30. Actionable Metrics
Actionable metrics are stats that are repeatable and improvable.
The importance of different analytics always depends on the goal of the team, but such metrics usually include stats like page load speed, average order value and product page views.
31. Hard Bounce
A Hard bounce happens when your marketing emails cannot be delivered because of permanent reasons.
It can happen, for example, because you tried to deliver to an incorrect email address or the recipient’s server blocked your email.
Hard bounce is not to be confused bounce rate, which refers to the number of visitors who leave your site after visiting only one page.
32. Soft Bounce
Soft bounce happens because of temporary reasons while sending running email campaigns.
For instance, the email box of the recipient was full or the message was too large to deliver.
33. Unique Visitors
The term unique visitors, when used in web analytics, is the number of people who visited your website at least once.
The difference between visits and visitors is that unique visitors are counted only once and visits indicate the total number of sessions on your website.
So, one person would represent one addition to your unique visitors, regardless of how many times they visited your page.
34. Customer Retention Rate (CRR)
Customer-Retention-Rate is growth hacking jargon that refers to the percentage of customers who remained with your business at the end of a given period of time.
It is a key metric to measure as marketers make huge efforts to attract visitors to their platforms and to convert them.
Calculate your CRR with the following formula:
E = Number of customers at the end of a period
N = Number of new customers acquired during that period (N)
S = Number of customers at the start of that period
Customer Retention Rate = ((E-N)/S)*100
35. Churn Rate
Simply put, this is the percentage of customers that stop interacting with your company during a given period. In growth hacking, it is usually expressed by the percentage of people who have cancelled their subscriptions.
Its impact is more significant in the case of SaaS and other subscription-based companies.
Use the following formula to calculate your customer churn rate:
(Lost Customers ÷ Acquired Customers) x 100%
Churn rate and customer retention rate are essentially two different ways of discovering the same thing: how well your business keeps customers.
Learn how to minimize your churn rate with Upodi.
36. CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)
Customer acquisition cost lays out the cost to your business of acquiring a new customer.
How to calculate CAC?
CAC= (All your marketing and sales expenses/number of new customers)

One reason businesses focus on their customer retention rate is that customer acquisition cost is significantly more expensive than the cost of retaining existing customers.
By prioritizing free organic channels and SEO, growth hackers strive to decrease the cost of acquiring new customers.
37. UTM Links
UTM links are a section of text that is added to your URL in order to allow you to determine where visitors have come from.
For example, adding a UTM link to an ad campaign or email campaign allows Google Analytics identify that your website received X number of visitors from these sources.
It is a useful way of measuring the success rate of your campaigns or to identify the best performing social media channels.
38. CTR (Click Through Rate)
Click-through rate is the proportion of users who clicked to your paid advertisement compared to people who it appeared for without clicking on it.
For example, if you run a Google Ads Campaign, your advertisement may receive 10 clicks and 100 impressions. In this case, your CTR is 10%.
While click-through rate is interesting, it’s not a wholly accurate metric as it doesn’t account for the people who view your ad, then directly search for your business rather than clicking the ad.
39. CPA (Cost per acquisition)
Cost per acquisition is a broader version of customer acquisition cost. Rather than focusing specifically on new customers, cost per acquisition covers the cost of acquiring new leads, users on a trial period, or even users on a free plan.
This metrics is useful for businesses who are looking for more detail on how much money they are spending on each stage of their funnel.
40. CPI (Cost per impression)
Every time your advertisement appears to someone from your target audience, it counts as an impression – though it’s worth noting that multiple impressions can be applied for one person.
Cost per impression is what it says in on the tin – it describes how much it has cost a business for each of these impressions.
It’s most commonly used within advertising to judge the price of campaigns.
41. Cost Per Thousand (CPM)
Cost per Thousand, which has the acronym CPM, is used to describe the cost of receiving 1000 impressions for an advertisement. For example, if an advertiser were charging $5 CPM, it would mean that a company would pay $5 for 1000 impressions of their ad.
42. Engagement Rate
Engagement rate is used across site analytics and social media to describe the rate at which people engage with your content. It is calculated by dividing a chosen metric for engagement by the total number of visitors or followers.
The engagement metric you use will vary by platform. For example, on websites you could you time on page or page per session. Meanwhile social media will often use the number of likes or comments.
Engagement Rate is an important indicator of user experience and customer engagement.
Ways to increase your engagement include:
- Creating gated content
- Collaborating with brands
- Interactive Content
- Storytelling
43. ROAS (Return on ads spend)
Calculating return on ads spend is fairly straightforward. You can measure how much revenue your ads generated by dividing the total revenue of your campaign by the expenses that the ad services came with.
It’s an important metric for any business to understand how much revenue is earned per currency unit spent on advertising.
44. OMTM (One Metric That Matters)
This term stands for a specific KPI that is extremely relevant to focus on compared to other metrics within a business.
In the case of growth hackers, it might be bounce rate, click-through rate, conversion rate, or another important digital marketing metric.
User Experience & Navigation Growth Hacking Jargon
In this section of our list of 99 growth hacking jargon terms, we’ll take a look at the different terminology around user experience on websites.
45. UX (User Experience)

User experience, or UX, describes how well your website is structured for your customers. It include factors like:
How fast does your website load?
How easy is it to find the information that your visitors look for?
How clickable is your site?
How credible is your webpage?
User experience also has an impact on your search ranking, as a website that is difficult to navigate will likely see a higher bounce rate.
46. Landing Page
When growth hackers try to bring traffic to websites, they will sometimes redirect visitors to a “landing page”.
Landing pages serve a specific function: lead generation. This could be by, for example, asking a visitor for their email address in exchange for a free resource.
Landing pages are often a logical extension of the email or ad from the which the visitor arrived, and can prove extremely effective at boosting sales.
Check out our Ultimate Landing Page Checklist for what to include in your landing pages.
47. Above the Fold
Above the fold content is the elements that first appear on your website without the need for users to scroll.
These elements vary wildly depending on the purpose of the site, but include features like value statements, call-to-action buttons, sign up forms, or welcome messages.
Carefully selecting the elements of your site that you want to appear above the fold is crucial, as this is the first impression visitors will have of your site.
48. Cookies
The purpose of cookies is to save your activities and information on different websites.
Companies use cookies in order to send more personalized and effective advertisements, improve user experience, or simply to save passwords and profile information.
Cookies are referred to by a number of different names, including HTTP Cookies or Web Cookies.
49. UI (User Interface)
While the terms UI and UX are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference. User interface includes every factor that determines a user’s experience on a digital platform.
So, for example, a search function that is present on all of your pages might be a positive user interface feature. But if it only shows information from your blog, it might not be a great user experience.
UI designers constantly improve usability, design and user experience in order to make platforms that are easier to use.
Find the Top UI Designers for 2021.
50. A/B testing
A/B testing is an important part of many forms of growth hacking and marketing.
By publishing two slightly different versions of the same asset, you are able to determine which is more successful at converting or engaging your customers.
Split testing is a similar process to A/B testing, but in this case two completely different versions of a marketing asset are shown to users.
51. ICE Score
This growth hacking jargon stands for Impact, Confidence, and Ease. This forms the fundamentals of an ICE score.
These terms are usually used while selecting the most promising A/B tests from your backlog.
Growth hackers score each of these elements on a scale of 1-10, resulting in a total score of 3-30.
The acronyms stand for the following:
- Impact: How big of an impact will the test have?
- Confidence: How sure are you that the test will lead to this impact?
- Ease: How easy is it to execute the test?
52. Call to Action (CTA)
Sign up, subscribe, try for free, get started, learn more, join us!
These are a few of the most common call to action examples that companies use to activate their users and move them to the next phase of their funnel.
Successful CTAs offer rewards, an explanation of what will happen after the action, frictionless forms, sometimes takes advantage of the fear-of-missing-out – or FOMO.
53. Domain Authority (DA), or Domain Ranking (DR)
Domain Authority and Domain Ranking are slightly different metrics that serve a similar purpose – namely to tell you how well regarded your website is.
Both range from 1 to 100, with higher scores awarded to websites that are better perceived by search engines.
Technically speaking, domain authority is a metric used by Moz to indicate the liklihood of a website ranking for a keyword, while domain ranking is a score awarded by Ahrefs and describes the quality of a site’s backlink profile.
54. Heatmap
Heat maps are visual representations of your customers’ interaction with your website.
There are four types of maps:
- Click tracking heat maps
- Scroll maps
- Mouse tracking maps
- Eye tracking maps.
Heat mapping is usually used to answer questions like:
How easily can customers find your subscription form?
How do visitors engage with your website?
Which colors are more attractive to your visitors?
55. RWD (Responsive Web Design)
Responsive web design revolves around providing the same experience while looking at a website, regardless of whether it is on a computer, mobile or tablet device.
Mobile device screens are smaller than computer screens, and users interact with touch rather than with a mouse.
This obviously has an effect on the design of a site. Responsive web design involves web developers optimizing their sites to automatically respond to the device a visitor is using.
User experience is a major factor in the algorithms of different search engines, and a site that is optimized for each type of device has therefore become an important part of achieving a high site or page ranking.
56. AWD (Adaptive Web Design)
The difference between the above mentioned RWD and Adaptive Web Design (AWD) is the way it conforms to different devices.
While RWD utilizes fluid elements, webpages that integrate AWD are built of CSS codes that respond to different display formats based on breakpoints.
Usually these webpages are designed based on the following six different screen widths.
- 320
- 480
- 760
- 960
- 1200
- 1800
57. Frictionless Forms
Frictionless forms make it easier to make an action with the least amount of effort on the part of your visitors.
For example, if you created a form that required a user to input their gender, age, location, it would not be considered to be a frictionless form. By requiring all of these fields, you are merely adding barriers to a visitor becoming a subscriber.
Frictionless forms use automatic sign up option and the least amount of information needed in order to make the customer journey as smooth as possible.
Growth Hacking Jargon Around Content

It’s shouldn’t come as surprise that the vast majority of SEO revolves around content. Content on a website can range from blog posts to videos and podcasts to white papers.
In this section, we’ll take a deep-dive into the growth hacking jargon and key terms that relate to content in marketing.
58. Smart Content
Personalized content for your visitors based on past behaviour and interest.
That’s smart content.
This kind of content changes, or is displayed in a different way, in order to conform to the interest of a specific visitor. It offers a more personalized and individual message to viewers.
By providing a more personalized experience, the goal of smart content is to achieve higher engagement or conversion rates from visitors.
59. Snackable Content
As the amount of daily information has been growing, it is getting harder and harder to grab readers’ attention.
This is where snackable content comes in.
Snackable content is information that is easy to process, usually visual, more to the point, and full of value.
It helps to generate leads, and increase user engagement and shares. It can encourage your visitors dive deeper in your product or other in-depth content pieces.
60. Second-Screen
Do you check your newsfeed while watching your favourite TV series?
Then you are using a second screen.
Marketers take advantage of this type of growth hacking jargon by advertising content that is relevant to the first screen to capture attention.
For example, if you’re watching a sports match on TV, you might be interested in more detailed statistics about one of the players. You’d then search for that information on your phone.
61. Clickbait
Clickbait content brings traffic by using the a catchy thumbnail or headline. One example of a clickbait headline would be “You’ll never believe what he looks like now…”
Clickbait headlines are often ultimately ineffective at retaining traffic, as the content rarely delivers on the promise made in the headline. This leads to a high bounce rate when visitors realize they have been tricked.
That said, incorporating some elements of clickbait writing into your headlines is not necessarily a bad thing – if the content you are sharing actually fits the headline you’ve used.
62. AI Content
AI content can take different forms. It is commonly where machines and computing software have capabilities for streamlining digital marketing processes and content which is automated with a minimum amount of human input.
AI generated content can be produced in the form of videos, presentations, images, emails, or even blog posts.
The Content Marketing Institute lists 6 AI tools to help in your content marketing.
There are new ai marketing tools for growth hacking launched all the time.
63. UGC (User generated content)
User generated content (UGC) is content which is produced by the customers of a business. It includes blogs, videos, or even posts on social media.
This kind of content is a free advertisement for any brand and it is used for digital marketing purposes frequently.
Check out these 10 real user generated content campaigns on Instagram.
64. Visual Storytelling
Visual storytelling is a great way of selling, grabbing attention and bringing emotion to your story or product.
You can utilize any kind of visual material in order to tell your story, including videos, images, infographics, or even memes.
65. X-Posting (Cross posting)
Simply said, cross posting is sharing the same message on different sections of the same platform (for example Subreddits) or on different platforms.
The message can be slightly modified based on the different audiences of each website but it is a simple, commonly used way of getting more traffic awareness and traffic.
66. Content Shock
As the amount of consumed content has been increasing, the level of engagement has been decreasing. This phenomenon is called content shock.
Digital marketers are increasingly using a range of different content marketing methods and it is becoming more challenging to stand out from the crowd and generate traffic.
67. Amplification
Amplification is growth hacking jargon that describes the process whereby a piece of content starts its journey across the channels of the digital world.
Sharing it through social media, emails, influencers or utilizing paid advertisements to drive traffic to your content are all frequently used techniques.
By using amplification, you improve your chances of obtaining backlinks, driving traffic to your website, or generating leads.
68. Backlog
Usually, backlog has two meanings in growth hacking. It can be a document where you collect, rank, sort and select your potential content ideas for future usage.
As writing content takes time, this preparation is highly advised in order to be ready to produce your content right at the time when it is necessary.
It can be also a backlog for A/B testing where you list potential tests to run in the future.
69. Advertorial
The expression advertorial comes from the word advertising and editorial. In digital marketing, these are platforms that publish sponsored articles.
These are great places to place backlinks pointing to your website or to describe your product.
70. FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
FOMO is a phenomenon where visitors make decisions based on the fear of missing out on something.
It is common among millenials and digital marketers who have been utilizing FOMO marketing techniques with great success.
There are many ways of taking advantage of this fear.
- Show to your visitors that other people are purchasing on your website
- Display the missed opportunities
- Let them know how many people are looking at the same item
- Create content that expires
- Use social proof
- Display user generated content
71. Interruption Marketing
With so much content, its become challenging to attract visitors and encourage them to perform any kind of action.
Interruption marketing involves interrupting your audience while they are performing a different task with your messaging.
This can often result in higher open rates or engagement, but does run the risk of irritating your audience.
It includes instant messages like exit intent pop-ups, live chats, cold email, or promotion updates.
72. Social Proof
Social proof describes the phenomenon where people make decisions based on the past behaviour and actions of others.
In growth hacking, it can take the form of rewards, testimonials, subscriber counts, media logos, reviews or a simple campaign emphasizing the number of satisfied customers.

We distinguish different kinds of social proof into:
- Expert social proof:
A credible person who forms the perception of other parties within the industry. - Celebrity social proof:
A well-known person, possibly with a wide group of followers, who is trusted for their endorsement. - User social proof:
A group of satisfied customers who are willing to share their experience with the brand. - Wisdom of crowd:
A large number of people who have already used the product. Highlight sections of your web page such as “most popular products”, “most visited pages” etc.
- Friends:
The most powerful form of social proof – recommendation for a product from a friend.
73. Micro moment
Micro-moments happen when a user turns to a device in the sour of the moment in order to answer a query or perform an action like buy something.
These moments are extremely valuable for marketers, as they represent the opportunity for “spur-of-the-moment” purchases.
Growth Hacking Jargon Around Strategy
Marketing strategy dictates the practices and goals of marketing campaigns, and as such is a crucial part of growth hacking. This section of the list covers the different growth hacking jargon around this area.
74. Agile
Agile digital marketing is all about deciding on the next steps of a marketing campaign based on results rather than following a pre-defined plan.
Cross functional teams and frequent iterations are key to an effective agile digital marketing strategy in order to provide high value results.
Making numerous small tests instead of a few larger ones, a data-focused approach that incorporates the past behaviour of your audience assists in allowing you to sat up-to-date, effective, and agile.
75. Customer Desire Map
Growth hackers use customer desire maps to understand visitors in more detail. These can be used to gain an insight into:
- Hopes & Dreams: what does a customer want to achieve?
- Fears & Pains: what are customers wanting to avoid?
- Barriers & Uncertainties: what is preventing a customer for taking action to achieve what they want?
By using this information, marketers and growth hackers are better able to create newsletters, websites, and content that converts.
76. OPA (Other People’s Audience)
Other People’s Audience, or OPA, refers to the practice of sharing your content with someone else’s audience. This usually entails using influencers, but can consist of other methods.
It is one way of rapidly growing your brand, as a popular figure within your niche is likely to have an audience that would be interested in your product.
There are few ways of doing it in digital marketing.
- Interviewing well-known people
- Influencer marketing
- Interacting with others within your niche on social media.
These are just a few ways of using OPA, but it’s a powerful way of increasing your own audience.
77. Traction Channels
The Traction Book was first published by Gabriel Weinberg & Justin Mares.
In their theory, they list 19 of the most important traction channels that can generate traffic for a business. These channels include:
- Viral Marketing – Does Viral marketing work in 2020?
- Public Relations – 5 things you should know about PR
- Unconventional PR
- Search Engine Marketing
- Social & Display Ads
- Offline Ads – 9 tips for making your offline ads super effective
- Search Engine Optimization
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Engineering as Marketing
- Targeting Blogs
- Business Development
- Sales
- Affiliate Programs
- Existing Platforms
- Trade Shows
- Offline Events – 10 offline event marketing to build a strong brand
- Speaking Engagements – Marketing with speaking engagements
- Community Building – 10 ways you can build a community around business social media
78. User Persona
A user persona is a broad representation of the customer that your marketing and sales team can go after.
What’s your ideal customers’ needs and pains?
What are their motivations?
What are their pains and how do their usual days look like?
What devices and social platforms do they use?
After identifying the characteristics of your fictional buyers you can shape your actions to serve their needs, provide true value to them, and be present on the platforms that they use.
79. Triple Peak Effect

In digital marketing, the Triple Peak Effect is growth hacking jargon that gives insights into the use and adoption of a new social media platform.
The Triple Peak Effect describes the three phases of the evolution of a social platform, and the hidden advantages that marketers can exploit in the different stages.
Users will begin using a new social media as either:
- Innovators: Typically the first to begin using a platform, members are willing to take risks, are very social, and typically in younger demographic.
- Early Majority: Influenced by the Innovators to join, F.O.M.O is often associated with this crowd. Large numbers join as the platform has been tested out and gained popularity by becoming entertaining and enjoyable.
- Late Majority (& laggards): Often sceptical of new social platforms & technologies, members in this group may typically have a focus of ‘keeping traditional’, the late majority and laggards are the final wave in user uptake.
Similar to the Technology Adoption Curve, the social media triple peak effect shows the return on interest over time and the rate of user uptake
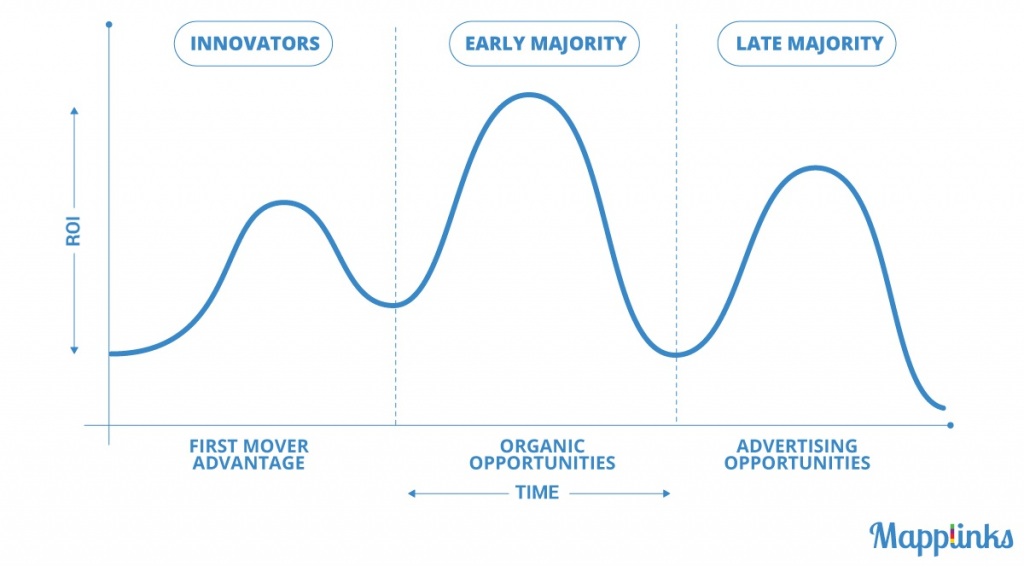
Innovators have the advantage of being first movers and to start to take advantage of the platform right after it has been launched.
Marketers targeting early majority users can take advantage of the organic traffic of the first wave of members that quickly become passionate about a new platform.
Finally, marketers are able to target the late majority. However, by this point awareness around the platform is at peak level and it requires significantly more effort and resources to beat competitors.
80. Outbound and Inbound
Outbound and inbound marketing describe two different methods of marketing to potential customers.
In its most basic sense, outbound marketing is when a company is the one who first interacts with the customer though ads, sales calls, or trade shows.
Inbound marketing is when a potential customer is the one who first interacts with a business. This can be via blog posts, subscribing to a mailing list, or videos.

Both of these forms of marketing have their pros and cons, and many of the best growth hackers use both inbound and outbound marketing channels.
81. Micro Influencer
Micro influencers are influencers who have between 10,000 and 50,000 followers on any of the social media platforms.
These influencers usually have niche audiences that can be fully targeted by brands that want to get promoted within a specific group of people.
Top micro-influencers by niche category have been put together on links blog. Performing influencer outreach is the first step to get started with them.
82. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is the process where an company or individual promotes the product of a company in return for a commission.
These parties usually have a wide network and numerous followers who can be influenced by the affiliate’s buyer behaviour.
83. Authority Marketing
Authority marketing is the process where brands and people strive to build an image representing themselves as experts and leaders in their industry.
Content marketing, referral marketing and media coverage are great ways of positioning yourself as an industry leader resulting in leads, customers, trust and a strong network.
84. Referral Marketing
Referral marketing is an extremely effective way of promoting your brand as an effect of social proof.
Even though it’s up to the person if he or she is willing to recommend your brand to others, there are certain techniques that you can utilize to increase the likelihood of referrals.
Make your content easy to share, partnering up with influencers, including a review section on your webpage or implementing a loyalty program can all help you increase referrals.
In order to track success, use the referral section in Google Analytics.
85. Real-Time Engagement
Real-time engagement is all about growth hacking jargon which describes using data that you collected about your future customers.
Instead of focusing on groups of users, following the journey of visitors who interact with your business’ website enables you to give personalized offers.
As an example, if your visitor is scrolling on your price list, it is probably time to contact them to close the deal. If your visitor has just found your products, spend time to interact and educate them about it to raise their interest.
86. Retargeting
97% of people who visit your website for the first time will leave without making a purchase.
At the same time, it is much easier to convert a past visitor to a customer than to acquire a new client.
Cookies are able to monitor visitors’ behavior on websites and advertise it later, making people revisit the webpage.
This is known as retargeting.
87. Newsjacking
Newsjacking is a creative way of selling your product or content by using a new trend or news and injecting it into your marketing.
For example, after the coronavirus pandemic, many companies adjusted the messaging to reflect a large change in society around the world.
88. Earned Media
Earned media is any publicity earned through any kind of action different to paid promotions.
This includes events like a company receiving a press release, when a business’ Tweet goes viral, when a brand’s article generates organic traffic or when users start writing positive customer reviews.
Earned media is harder to generate but the rewards have a huge impact. It is a highly cost efficient method of marketing.
Here’s a few tips to generate earned media:
- Focus on customer satisfaction
- Create content that is worth sharing
- Interact on social media
89. Omnichannel
Omnichannel marketing is a strategy that strives for a company to be available to customers across multiple communication channels to reach the customer.
It aims to create a seamless shopping experience by utilizing tools across multiple customer touch-points.
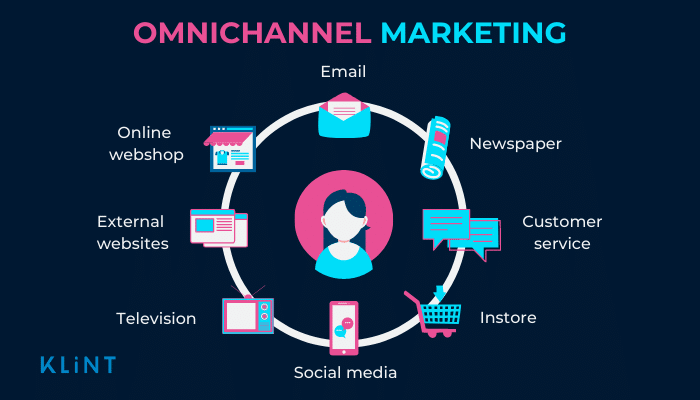
This can be in the form of both and physical presence such as:
- Newsletters
- Emails
- Printed type (including newspapers, magazines & leaflets)
- Social media handles & posts
- Paid ads
- Banner displays
- Websites (including third party websites)
- Television & radio
- Instore
- Customer services
- Telephone
Omnichannel marketing theory assumes that users may start their customer journey on one channel and after bouncing on numerous others, they eventually become customers.
90. Lead Nurturing
During lead nurturing, digital marketers, growth hackers and business developers develop relationships with potential customers at each stage of the sales and marketing funnel.
There are numerous ways to of lead nurturing, including:
- Using proactive live chats
- Call to Action (CTA) buttons
- Targeting the right audience to share your content with
- Organizing webinars
91. Marketing Funnel
The elements of the marketing funnel represent the stages of a customer journey starting from awareness to purchase.
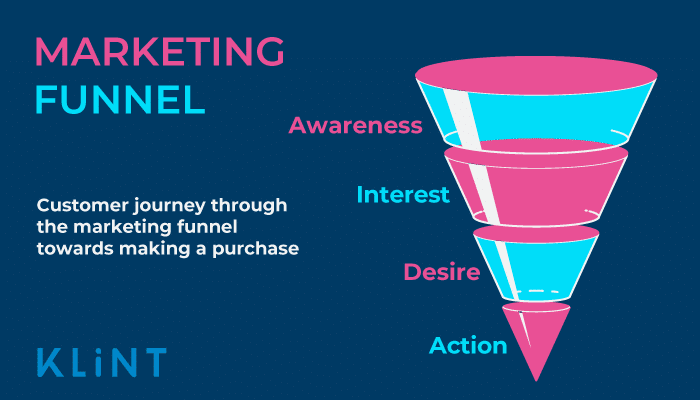
These stages are:
- Awareness: The future customer gets aware of the product
- Interest: The visitor discover the content, product, or service that raises his or her attention
- Desire: The person perceives the offer as valuable and feels desire to purchase it or interact with the brand
- Action: The prospects make the buyer decision
More in-depth marketing funnel templates include the stages “loyalty” and “advocacy” where the customer repeat purchases in the future and recommends it to others.
92. Activation
Activation is an action that motivates your customers to move to the next phase of your marketing or sales funnel faster than they would do it by themselves.
93. Account Based marketing
Account based marketing is a more personalized approach of acquiring new, usually high-value customers.
Marketers target individuals associated with a specific account and develop a highly personalised account relationship rather than targeting the whole industry
94. PPC (Pay Per Click)
Pay-per-click is an advertising model where the advertiser pays to the search engine after every click an advertisement generates.
Search engines just as Google, Yahoo, Twitter or Facebook implemented this method in their business model, offering promotion services to their customers.
95. T-Shaped Marketer
T-shaped marketers are professionals who have knowledge within all the different fields of marketing and a deeper, in-depth understanding of a few specific elements of it.
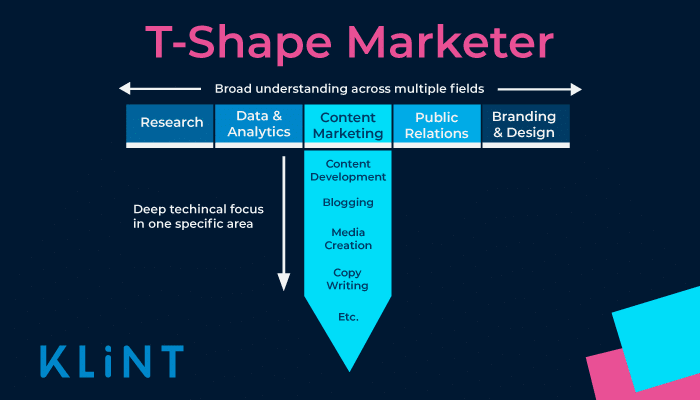
As an example, a T-shaped digital marketer has knowledge about design, content, paid, PR, SEO, community, social and all the other major fields. He or she is an expert of Facebook management, influencer marketing and Instagram growth under the umbrella of social media.
96. Quick Win
In growth hacking, quick wins include any kind of steps that results in a relatively big impact in a short period of time.
For example, improving site speed, launching SoMe campaigns and email campaigns or registering on Google My Business.
97. Social Signals

Social signals include social media shares, likes, votes, views and other activities on webpages such as LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram or Reddit.
Signals can include:
- Content Shares
- Likes
- Comments
- Mentions
These signals indicate the popularity of a piece of content while Search Engines determine your ranking.
98. Scraping
Scraping is growth hacking jargon that is usually done by developers. It refers to the practice of extracting information from other websites.
They can do it for a number of reasons, including:
- Building up sales pipelines
- Using tools from competitors
- Finding possible websites to receive backlinks from.
It is usually done using web scraping extensions tools.
99. Event Triggered Email

Event triggered emails are directed communications sent out based on actions that page visitors made on a webpage. Ever received an email after signing a newsletter on a website you’re reviewing? That is event triggered emailing.
This data-driven-method helps to leverage on the desired action of potential new customers and motivates them to perform the right action at the right time.
It often can be used to drive the viewer towards a purchase on e-commerce sites through offering an incentive specifically for visiting the page or signing to the newsletter.
Did your visitor read a blog post on your website? Send out an email about the same topic. Did he or she visit the product page? Then it is time to send a good offer or more information.
Conclusion
Digital Marketing can be confusing, and it doesn’t help that there are so many different marketing keywords that you need to know.
In order to be a successful growth hacker, growth hacking jargon will help you to understand what all these functions and metrics are about.
This digital marketing glossary covers the vast majority of growth hacking jargon. However, it is important understand that the industry is constantly evolving, and what is relevant now will no longer be tomorrow.
Check our list of growth hacking jargon for the latest terminology.





Digital Marketing is confusing, and it doesn’t help that there are so many different marketing keywords that you need to know. Some are abbreviations and some are new words. Coming from one growth hacker to another, the growth hacking jargon will help you understand what all these functions and metrics are about.